A Beginners Guide to Dart - The Tooling Ecosystem - Part Nine
6 comments

Repository
https://github.com/dart-lang/sdk
What Will I Learn?
- You will learn about the Dart Tool Pipeline
- You will learn about the Pub Tool
- You will learn how to install external dependencies in Dart
- You will learn how to use the Observatory in Dart
- You will learn about the Testing suites that exist for Dart
Requirements
System Requirements:
- IDEA intellij or Visual Studio Code with the Dart Plugins
- The Dart SDK
OS Support for Dart:
- Windows
- macOS
- Linux
Required Knowledge
- The Dart SDK
- A Dart supported text editor (Dart Pad can be used)
- A little time to sit and watch a video and some patience to learn the language
Resources for Dart:
- Dart Website: https://www.dartlang.org/
- Dart Official Documentation: https://www.dartlang.org/guides/language/language-tour
- Dart GitHub repository: https://github.com/dart-lang/sdk
- Awesome Dart GitHub Repository: https://github.com/yissachar/awesome-dart
- Pub website: https://pub.dartlang.org
Sources:
Dart Logo (Google): https://www.dartlang.org/
Difficulty
- Beginner
Description
In this Dart video tutorial, we finish off the beginners guide by looking at the tooling pipeline for the Dart programming language. This includes taking a look at the Pub tool; a tool which helps manage dependencies and allows developers to install and use global executables like Stagehand or Webdev. We also look at the Dart Observatory which is a built in profiling tool that allows you to look at the CPU and memory footprint of your applications and their isolates. And finally we finish by looking at the default test suite and how it can be used for test driven development.
Managing Dependencies and Global Executables with Dart's Pub Tool
The Pub tool is Dart's primary way to managing packages. It is similar to other dependency management tools like JavaScript's NPM, Elixir's Mix and Rust's Cargo. The Pub tool allows developers to define a pubspec.yaml file with metadata inside of it. This metadata is then read by the CLI and used to build the project. The Pub tool also allows developers to install and eternal CLI executables.
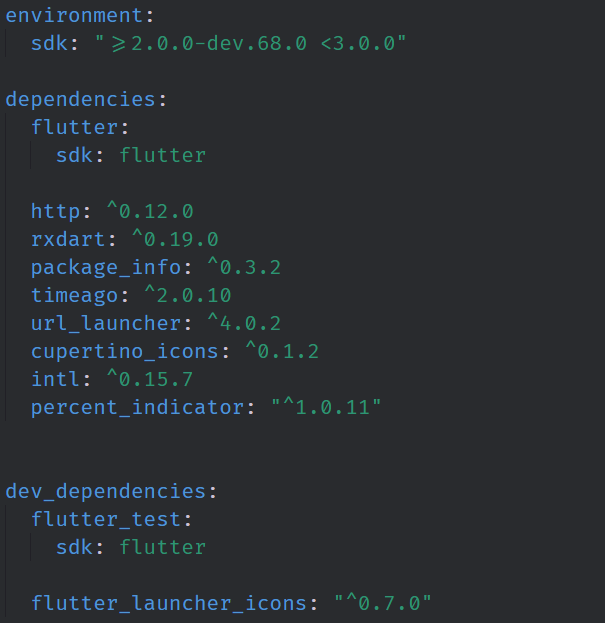
Above is an example of a pubspec.yaml file for a fully functional flutter application. By default, all dart apps must contain an environment key; this key tells the pub tool which virtual machine to use when running the application. In this case, we want to use a version of the Flutter SDK that is greater than 2.0.0-dev.68.0 but less than version 3.0.0. Below this key is a dependencies key which defines what third party dependencies are needed to run this application. Below the dependencies key is a dev_dependencies key which defines dependencies that are needed in development but not needed when the application is published.
Profiling an Application with the Dart Observatory
The Dart Virtual machine also features a profiling tool called the Observatory. This tool allows the developer to peek into a running Dart virtual machine instance and it provides live data and state for your project. You can use the Observatory to determine how the memory is allocated, how the application's code is spending its execution time, which lines of code are being executed, and how the CPU is handling the load. The Observatory is often used to debug memory leaks and memory fragmentation.
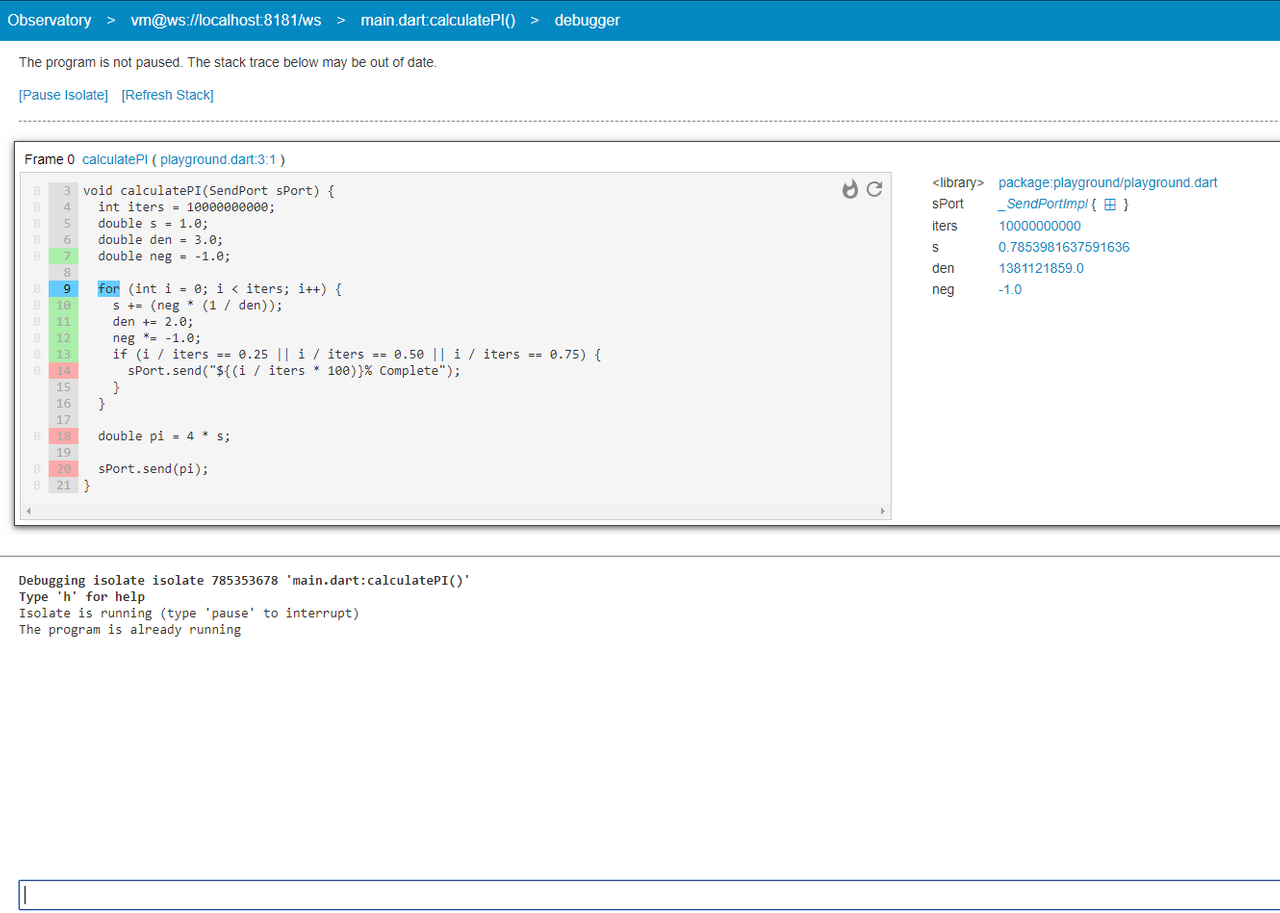
Above is an image of the Dart Observatory's debugger window. The Graphical user interface (GUI) for the Observatory is served via a web server which runs on the Dart Virtual Machine. You are then able to access the Observatory by pointing a browser at localhost:8181. Notice that the debugger shows the code that is being executed on the left hand side of the screen. On the right hand side of the screen is a cross section of the state at that given moment; with each variable showing its current value. On the bottom is a command prompt that allows the user to manipulate the code in ways that are useful to debug the application. This includes pausing the code, stepping backwards through the state, pushing the code forward line by line and directly modifying the state.
The Source Code for this video may be found here: https://github.com/tensor-programming/dart_for_beginners/tree/tensor-programming-patch-8
Video Tutorial
Curriculum
- A Beginners Guide to Dart - Concurrency, Asynchronous Evaluation and Parallelism in Dart - Part Eight
- A Beginners Guide to Dart - Generics, Exceptions, Factory Constructors, and Enumerated Types - Part Seven
- A Beginners Guide to Dart - Scope, Iterators, Functional Programming and Collections - Part Six
- A Beginners Guide to Dart - Inheritance, Abstract Classes, Interfaces, Mixins and Casting - Part Five
- A Beginners Guide to Dart - Methods, Final, Static, and Class Inheritance - Part Four
- A Beginners Guide to Dart - Intro to Classes and Objects - Part Three
- A Beginners Guide to Dart - Control Flow and Low Level Compilation - Part Two
- A Beginners Guide to Dart - Types, Functions, Variables and Objects - Part One
Comments